目標
前回(下記参照)は,Compute Shaderを使って,3DCGを描画した際に生成されるZバッファの線形化を行うプログラムを作成した.今回は,RGB-D画像を用いて,頂点・法線マップを生成するプログラムを作成する.尚,RGB-D画像は,Zバッファの様に非線形化は行われていないため,線形化する必要はありません.
実装環境
- Windows 10 64bit
- Visual Studio 2015
- GLEW 3.2.1
- 設定方法はこちらを参照
- GLEW 1.13.0
- 設定方法はこちらを参照
- GLM
- 設定方法はこちらを参照
- DevIL
- 設定方法はこちらを参照
- OpenCV
- 設定方法は外部のWebサイトを参照
- 尚,contribは必要なし
処理内容
流れ
- RGB-D画像読み込み
- TUM RGB-D Dataset等から適当なものをダウンロードしておく
- もしくは,自らKinectやXtionから取得しておく/実時間で取得する
- Compute Shaderを使って頂点マップを生成
- 頂点マップとは,RGB-D画像の各画素に対応するfloat型3チャンネルの画像
- Compute Shaderを使って法線マップを生成
- 法線マップとは,RGB-D画像の各画素に対応するfloat型3チャンネルの画像
- 生成した頂点・法線マップを描画
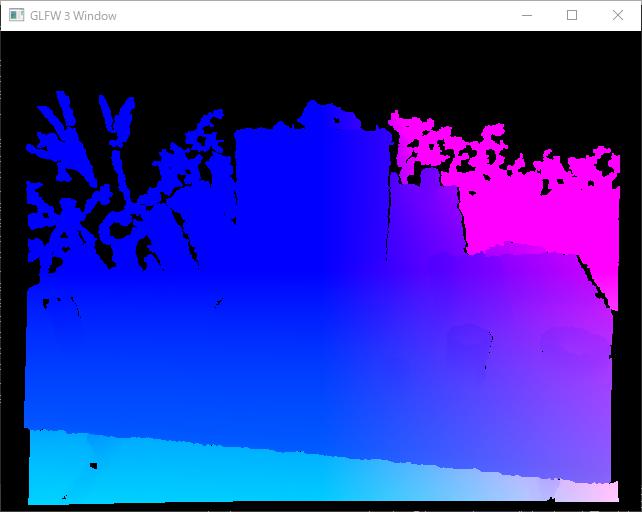
頂点マップの計算
参考文献1の3章によると,以下の式によって,フレーム目の奥行マップ
から
フレーム目の頂点マップ
が生成できる.
この時,は画像上の2次元位置,
は求めたい頂点マップ
の
に対応する頂点,
は
に対応する奥行値,
は事前の校正により既知である内部パラメータ行列を表す.
「」の部分は,出力される
が実数の3次元ベクトルであることを表しているだけである.尚,ここでは,1フレーム(1枚の画像)のみ入力することを考えて,
は無視する.以上より,シェーダで記述する式は以下のようになる.
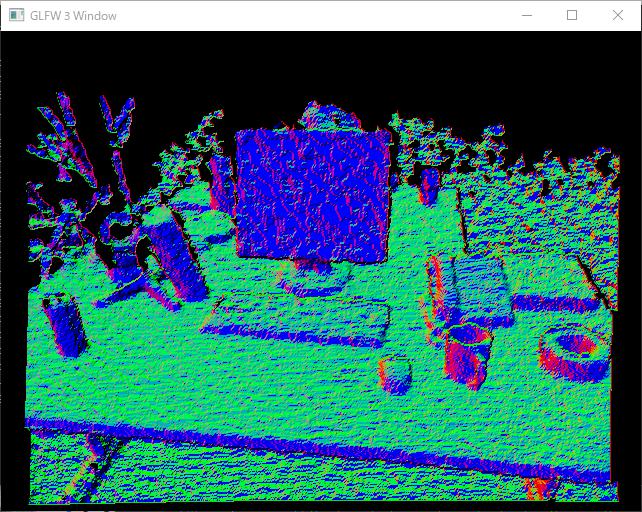
法線マップの計算
ここでも参考文献1の3章に倣って,Central Differenceを取ることで,頂点マップから法線マップ
を計算する.具体的には,法線マップ
の要素
以下の式より求める.
尚,は,ベクトル
を正規化する関数である.
サンプルプログラム
前回までのプログラムをそのまま利用し,以下の様に書き換えます.
main.cpp
- csCalcVertMapクラス Compute Shaderを使って,奥行マップから頂点マップを生成するためのクラス.
- csCalcNormMapクラス Compute Shaderを使って,頂点マップから法線マップを生成するためのクラス.
- キー操作 「2」「3」キーを押すと,それぞれ頂点マップ,法線マップが表示される.それ以外を押すとRGB画像が表示される.
#include <glm/glm.hpp> #include <glm/ext.hpp> #include <glm/detail/setup.hpp> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include "OpenGLWrapper/window.h" #include "OpenGLWrapper/shaderUtil.h" #include "OpenGLWrapper/modelTex.h" #include "OpenGLWrapper/rgbdTex.h" // Vertex map calculation class csCalcVertMap : public gl::compShader { private: const glm::mat3 K; // Intrinsic parameters public: csCalcVertMap( int w, int h, const glm::mat3 &K, const string &compShaderName ) : gl::compShader(w, h, 1, GL_RGBA32F, GL_RGB, GL_FLOAT, compShaderName), K(K) { glUseProgram(prog); { // Update the uniform GLuint locInvK = glGetUniformLocation(prog, "invK"); glUniformMatrix3fv(locInvK, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(glm::inverse(K))); } glUseProgram(0); } void csCalcVertMap::execute( GLuint inTexID ) { glUseProgram(prog); { // Input texture glBindImageTexture(0, inTexID, 0, GL_FALSE, 0, GL_READ_ONLY, GL_R32F); // Output texture glBindImageTexture(1, texID, 0, GL_FALSE, 0, GL_WRITE_ONLY, GL_RGBA32F); glDispatchCompute(width / 32, height / 32, depth); } glUseProgram(0); } }; // Normal map calculation class csCalcNormMap : public gl::compShader { public: csCalcNormMap( int w, int h, const string &compShaderName ) : gl::compShader(w, h, 1, GL_RGBA32F, GL_RGB, GL_FLOAT, compShaderName) { } void csCalcNormMap::execute( GLuint inTexID ) { glUseProgram(prog); { // Input texture glBindImageTexture(0, inTexID, 0, GL_FALSE, 0, GL_READ_ONLY, GL_RGBA32F); // Output texture glBindImageTexture(1, texID, 0, GL_FALSE, 0, GL_WRITE_ONLY, GL_RGBA32F); glDispatchCompute(width / 32, height / 32, depth); } glUseProgram(0); } }; class MyWindow : gl::window { private: csCalcVertMap *myCSCalcVertMap; csCalcNormMap *myCSCalcNormMap; gl::rgbdTex *myRGBDTex; gl::modelTex *myModelTex; public: MyWindow( int w, int h, const string &wndName, const glm::mat3 &K, // Intrinsic parameters const float factor, // See: http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/file_formats#intrinsic_camera_calibration_of_the_kinect const string &colorImgName, const string &depthImgName, const string &compVertMapShaderName, const string &compNormMapShaderName ) : window(w, h, wndName) { // Read images cv::Mat imgC = cv::imread(colorImgName); // Color image cv::Mat imgD = cv::imread(depthImgName, -1); // Depth image imgD.convertTo(imgD, CV_32F); imgD /= factor; // Upload the RGB-D image to your GPU myRGBDTex = new gl::rgbdTex(imgC.cols, imgC.rows); myRGBDTex->updateRGBDTex(imgC.data, imgD.data); // Create computer shaders myCSCalcVertMap = new csCalcVertMap(imgC.cols, imgC.rows, K, compVertMapShaderName); myCSCalcNormMap = new csCalcNormMap(imgC.cols, imgC.rows, compNormMapShaderName); // Create a texture polygon to display the results myModelTex = new gl::modelTex(imgC.cols, imgC.rows, "../shader/modelTex.vert", "../shader/modelTex.frag"); } ~MyWindow() { if (myRGBDTex) { delete myRGBDTex; myRGBDTex = NULL; } if (myCSCalcVertMap) { delete myCSCalcVertMap; myCSCalcVertMap = NULL; } if (myCSCalcNormMap) { delete myCSCalcNormMap; myCSCalcNormMap = NULL; } if (myModelTex) { delete myModelTex; myModelTex = NULL; } } void render() { const glm::mat4 rotMat180X = glm::rotate(glm::pi<float>(), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)); myModelTex->setModelMat(rotMat180X); // Rendering loop while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(wnd)) { // Clear color and depth buffers glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Calculate a vertex map from a depth map myCSCalcVertMap->execute(myRGBDTex->getDepthTexID()); // Calculate a normal map from a depth map myCSCalcNormMap->execute(myCSCalcVertMap->getTexID()); // Show the results switch (keyID) { case '2': // Vertex map myModelTex->render(myCSCalcVertMap->getTexID()); break; case '3': // Normal map myModelTex->render(myCSCalcNormMap->getTexID()); break; default: // Color image myModelTex->render(myRGBDTex->getColorTexID()); break; } // Swap front and back buffers glfwSwapBuffers(wnd); // Poll for and process events glfwPollEvents(); } } }; int main() { glm::mat3 K(525.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 525.0f, 0.0f, 319.5f, 239.5f, 1.0f); MyWindow wnd( 640, 480, "GLFW 3 Window", K, 5000.0f, "../data/1311868164.363181.png", "../data/1311868164.338541.png", "../shader/calcVertMap.comp", "../shader/calcNormMap.comp" ); wnd.render(); return 0; }
calcVertMap.comp
csCalcVertMapクラスで利用されるシェーダプログラム.頂点マップの計算をシェーダプログラムとして,具体的に書きだした.
#version 430 layout (binding = 0, r32f) readonly uniform image2D dataIn; // Depth map layout (binding = 1, rgba32f) writeonly uniform image2D dataOut; // Vertex map uniform mat3 invK; // Inverse of the intrinsic matrix layout (local_size_x = 32, local_size_y = 32) in; void main(void) { ivec2 u = ivec2(gl_GlobalInvocationID.xy); float z = imageLoad(dataIn, u).r; vec3 v = z * invK * vec3(u, 1.0); imageStore(dataOut, u, vec4(v, 1.0)); }
calcNormMap.comp
csCalcNormMapクラスで利用されるシェーダプログラム.法線マップの計算をシェーダプログラムとして,具体的に書きだした.
// REF: http://answers.opencv.org/question/82453/calculate-surface-normals-from-depth-image-using-neighboring-pixels-cross-product/ #version 430 layout (binding = 0, rgba32f) readonly uniform image2D dataIn; // Depth map layout (binding = 1, rgba32f) writeonly uniform image2D dataOut; // Normal map layout (local_size_x = 32, local_size_y = 32) in; void main(void) { vec3 xyz[4] = { imageLoad(dataIn, ivec2(gl_GlobalInvocationID.xy) - ivec2(1, 0)).rgb, imageLoad(dataIn, ivec2(gl_GlobalInvocationID.xy) + ivec2(1, 0)).rgb, imageLoad(dataIn, ivec2(gl_GlobalInvocationID.xy) - ivec2(0, 1)).rgb, imageLoad(dataIn, ivec2(gl_GlobalInvocationID.xy) + ivec2(0, 1)).rgb }; vec3 vecX = xyz[1] - xyz[0]; vec3 vecY = xyz[3] - xyz[2]; imageStore( dataOut, ivec2(gl_GlobalInvocationID.xy), vec4(normalize(cross(vecX, vecY)), 1.0) ); }
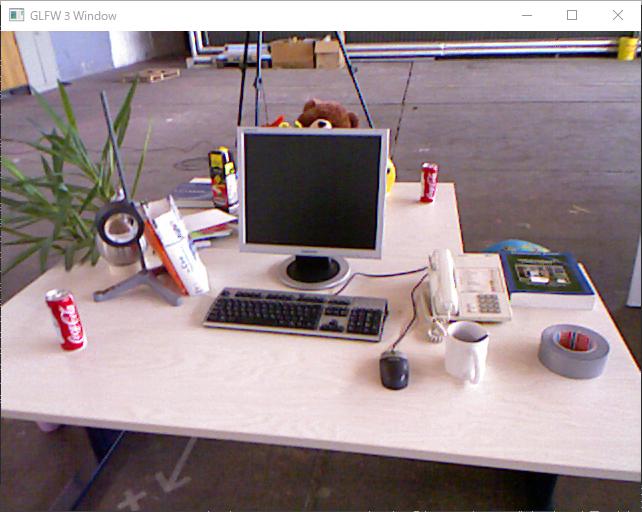
結果
以下に示す,RGB画像,奥行マップ,頂点マップ,法線マップにある通り,目標達成!尚,奥行マップを表示させるようにはしていないので,これは入力画像をそのままここに載せている.
正直なところ,TUM RGB-D Datasetでのカメラ座標系の向き,OpenGLのカメラ座標系との関係が分かっていないので,画像だ出ただけ,と言えばそれだけ.座標軸が想定通りか,今後,検証する必要がある.また,法線マップがガタガタなので,次回はBilateral Filterを実装してみようと思う.